ObjectInputStream enables us to read Java objects from an InputStream. We wrap an InputStream in a ObjectInputStream and then you can read objects from it.
Normally we will use the ObjectInputStream to read objects written (serialized) by a Java ObjectOutputStream.
Please visit Serialization in Java for more on Serialization topic.
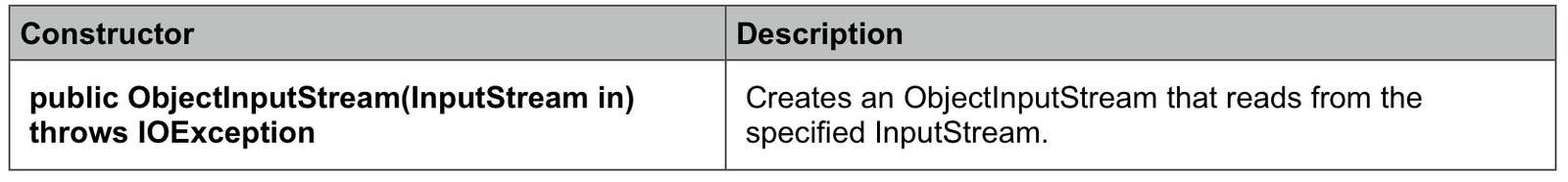
Constructor
Example
In the below example, we will write(serialize) an Employee Object to a text file and then read(deserialize) the Employee Object back from the file.
package com.java.io;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class ObjectStreamExample {
public void writeObjectToFile() {
FileOutputStream fos = null;
ObjectOutputStream oos = null;
try {
Employee employee = new Employee("Gyan", 5);
fos = new FileOutputStream("/Test/TestFolder/test-file7.txt");
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(fos);
//Writing Object to File
oos.writeObject(employee);
oos.flush();
System.out.println("Data Employee Object to File");
} catch (IOException ioe) {
ioe.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// Closing the streams
if (fos != null)
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (oos != null)
try {
oos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public void readObjectFromFile() {
FileInputStream fis = null;
ObjectInputStream iis = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream("/Test/TestFolder/test-file7.txt");
iis = new ObjectInputStream(fis);
//Reading Object from File
Employee retrievedEmployee = (Employee) iis.readObject();
System.out.println("retrievedEmployee:" + retrievedEmployee);
} catch (IOException ioe) {
ioe.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// Closing the streams
if (fis != null)
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (iis != null)
try {
iis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ObjectStreamExample objectStreamExample = new ObjectStreamExample();
objectStreamExample.writeObjectToFile();
objectStreamExample.readObjectFromFile();
}
}
class Employee implements Serializable {
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee [name=" + name + ", id=" + id + "]";
}
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1 L;
public Employee(String name, Integer id) {
this.name = name;
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
private String name;
private Integer id;
}Data Employee Object to File
retrievedEmployee:Employee [name=Gyan, id=5]File

