ByteArrayOutputStream implements an output stream in which the data is written into a byte array. The buffer automatically grows as data is written to it. The data can be retrieved using toByteArray() and toString().
Closing a ByteArrayOutputStream has no effect. The methods in this class can be called after the stream has been closed without generating an IOException.
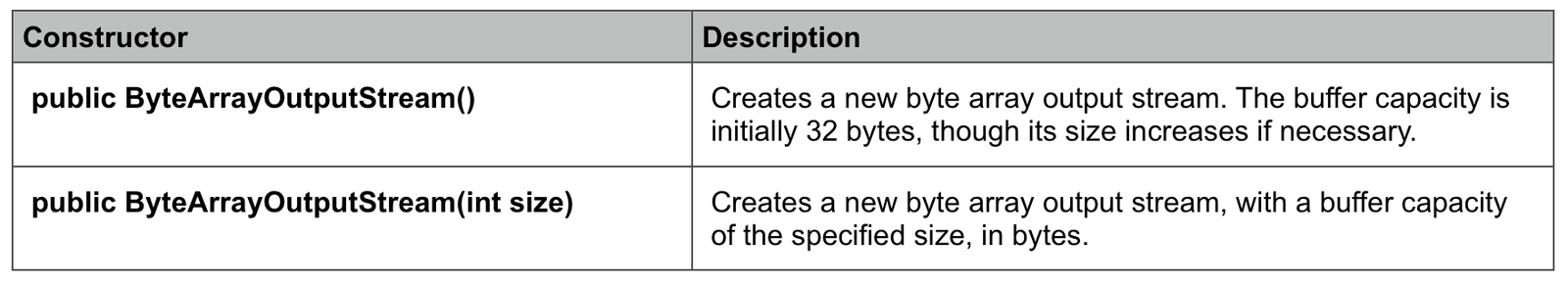
Constructors
Methods

package com.java.io;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ByteArrayOutputStreamExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = null;
try {
byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byteArrayOutputStream.write(" data1 ".getBytes());
byteArrayOutputStream.write(" data2 ".getBytes());
byteArrayOutputStream.write(" data3 ".getBytes());
byte[] bytes = byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray();
for (int i = 0; i < bytes.length; i++) {
System.out.print((char) bytes[i]);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// Closing the streams
if (byteArrayOutputStream != null)
try {
byteArrayOutputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}data1 data2 data3 Related Article
